For Teachers
The Challenge
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a classification of levels of thinking. Created by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues in 1956 and revised in 2001 by psychologists, this framework influences educators. This taxonomy is useful if and when educators can find practical applications to their classroom instruction.
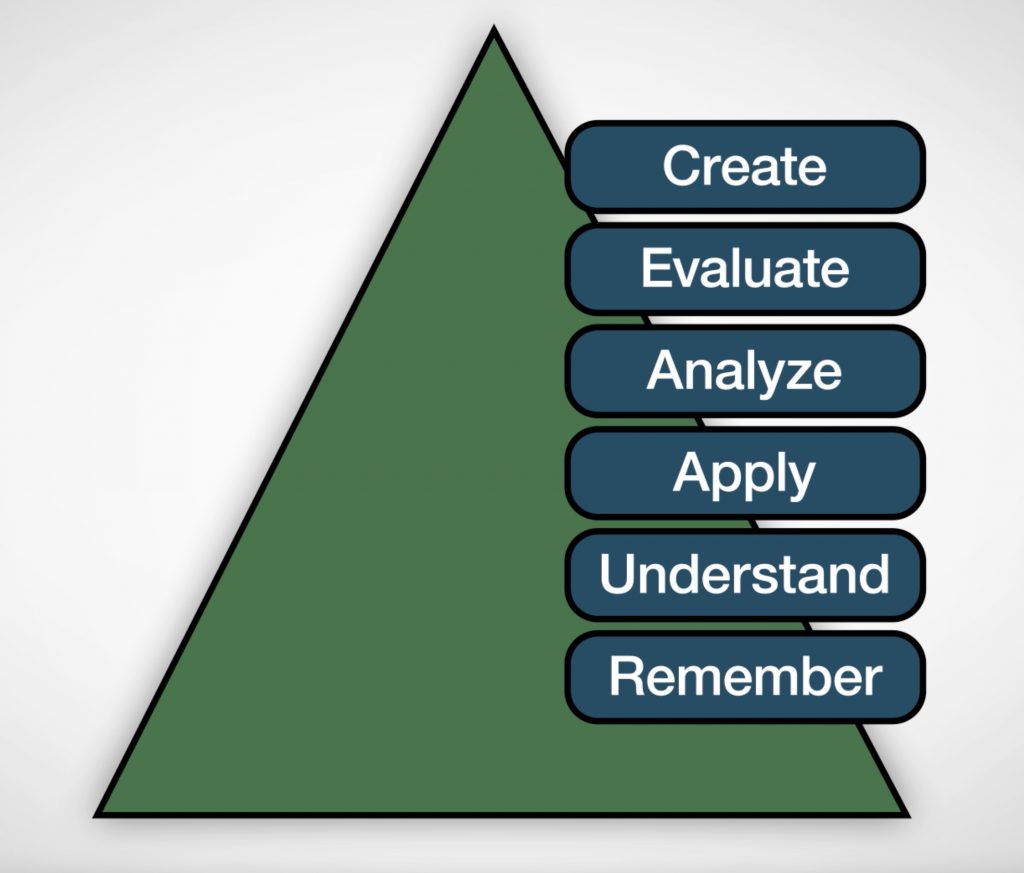
Bloom’s Taxonomy
There are six levels of thinking within the taxonomy that are divided into two categories: low and high level. Low level thinking guides students to high-level thinking. Low level thinking builds a foundation of understanding. High level thinking develops a deeper understanding of content. High level thinking is necessary to solve problems.
Asking Questions
Within the gradual release of responsibility, students listen and respond during direct instruction. An effective teacher asks simple and complex questions during a direct instruction lesson because learners are not passive listeners. Questions motivate and engage students. They lead to a deeper understanding of content as they allow teachers to interact with students. Bloom’s Taxonomy is also useful to teachers during guided practice when students work in pairs while the teacher challenges, reviews or reteaches the lesson.
Writing Lesson Plan Objectives
Bloom’s Taxonomy can also be applied to writing lesson plan objectives or learning outcomes for each step of the gradual release of responsibility. A well-written objective states what the student will be able to do at the end of the lesson. Choosing the appropriate action verb in an objective is critical. Action verbs found in Bloom’s Taxonomy guide the teacher in the preparation and desired outcome of the lesson.
During the third step of the gradual release of responsibility, students complete a task to demonstrate mastery during independent practice. Teachers write an objective for a lesson plan using an action verb that correlates with designing a task to demonstrate mastery. Bloom’s Taxonomy is a great resource for choosing the best action verb.
Benefits
An effective teacher considers Bloom’s Taxonomy to deepen a student’s thinking. It is a widely accepted hierarchy of low and high levels of thinking. It can be applied to questioning techniques and it guides a teacher to choose the appropriate action verbs in lesson planning.
Creativity follows mastery, so mastery of skills is the first priority for young talent.
– BENJAMIN BLOOM
We believe in you!
We train teachers to ask questions and write lesson plan objectives utilizing Bloom’s Taxonomy. If you want to impact teachers and school leaders in your community, send us a message.
Beth is the President of Teaching Training Together, an organization based in Burlington, Massachusetts, that provides initial training through professional development seminars to underserved school leaders and teachers.
